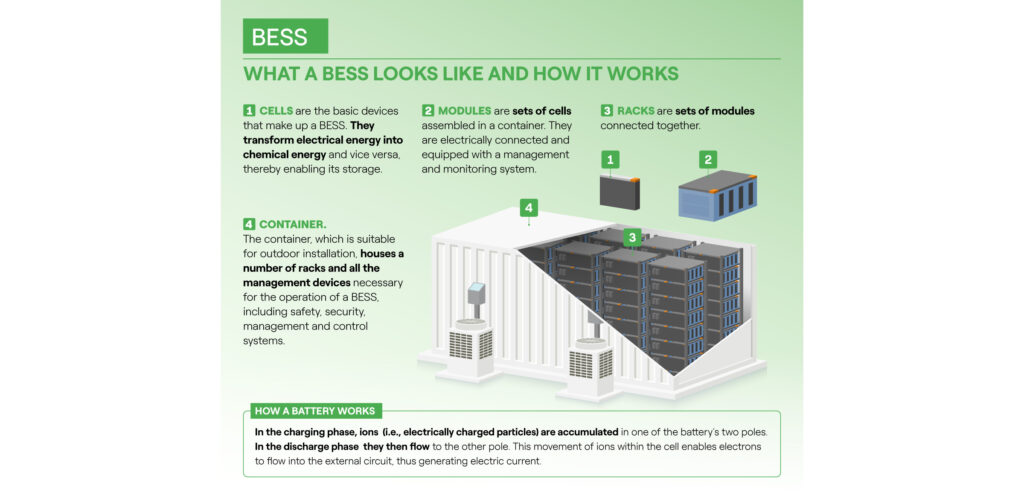
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) are a key element in the energy transition, with several fields of application and significant benefits for the economy, society, and the environment.
- BESS are the power plants in which batteries, individually or more often when aggregated, are used to store the electricity produced by the generating plants and make it available at times of need.
- The fundamental components of a Battery Energy Storage System are the blocks formed by the batteries, but other elements are also present. They are namely: an inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) from the batteries to the alternating current (AC) from the Grid (and vice versa); a transformer, for adapting the system’s voltage to that of the Grid; and finally, auxiliary systems (particularly for cooling and fire-fighting).
- The technology for BESS is based on the use of electrochemical storage, which can store the energy produced by renewable power plants. It’s a kind of power bank that can give back stored energy, by returning it on demand.
- BESS are one of the main energy storage system: sometimes they are also called electrochemical energy systems to distinguish them from others, such as gravitational energy systems (including pumped-storage hydroelectric power plants), mechanical energy systems (including compressed air or flywheel systems) and (Thermal Energy Storage, TES) systems
- As in all storage systems, in the case of BESS the electricity produced by a power plant, or any other generating plant (even a single photovoltaic panel), is stored and then released at the desired times and moments. BESS uses a specific technique for storage: since an electric current is a flow of electrical charges, a battery is charged by accumulating charges of particular materials (called electrolytes) at one of the two poles, from which they then flow to the other pole in the discharge phase.